Anatomy and Cell Biology 2221 Study Guide - Fall 2018, Comprehensive Midterm Notes - Anatomical Terms Of Motion, Sternum, Scapular

Anatomy and Cell
Biology 2221
MIDTERM EXAM
STUDY GUIDE
Fall 2018


Anatomy – Lecture 1
Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical position: anatomical terminology refers to this position
Anatomical planes: pass through the body which provide frame of reference in
3D
Directional Terminology
• Right/Left → cadaver specific, not the viewers left and right
• Anterior (Ventral)/Posterior (Dorsal)
• Superior (Cranial)/Inferior (Caudal)
• Medial/Lateral
• Proximal/Distal
Body Composition – 4 Basic Tissues
1. Epithelia: classified based on cell morphology & number of layers
2. Nervous Tissue: main component of brain, spinal cord, nerves
3. Muscle tissue: contractile tissue controlled either voluntarily (skeletal muscle) or
involuntarily (cardiac & smooth muscle)
4. Connective Tissue:
• Proper: loose (functions as a binding tissue ex adipose) & dense (resists mechanical
stress ex. ligs, tendons, deep fascia)
• Blood: transport medium for gases, nutrients, waste
• Bone: supports and protects organs and the attachment site for muscles
• Cartilage: provides cushion and support ex) hyaline (covers ends of bone), fibrocartilage
(intervertebral discs)
Fascia
“uperfiial Fasia Hypodermis elow the dermis
• Contains adipose
• Fat storage
• Passageway for nerves and blood vessels
Deep Fascia
• Dense regular connective tissue
• Creates compartments surrounding individual and groups of
muscles and large vessels & nerves
• Reduces friction during muscle contractions
Joints
→ These are sites where two or more bones meet. They provide
stability, and/or mobility to the skeleton.
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis
Deep Fascia
(white)
X-section of forearm
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
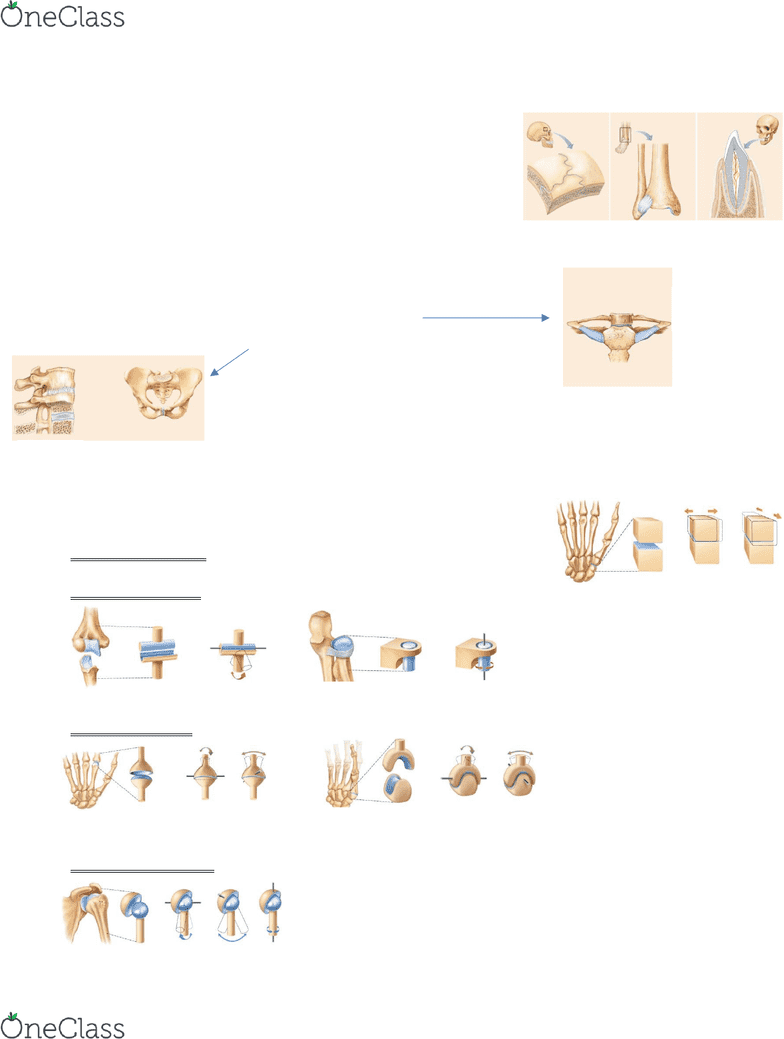
Classified either funtion OR struture…
• Functional: immovable, slightly moveable, freely movable
• Structural: fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
Fibrous Joints: connected by dense regular connective tissue, lack a
joint cavity
1. Sutures → b/w skull bones, immovable
2. Syndesmoses: connected by ligaments, movement range depends on length
3. Gomphoses: peg-in-socket joint for root of tooth
Cartilaginous Joints: bones united by cartilage, lack a joint cavity
1. Synchondroses: hyaline cartilage, immovable
2. Symphyses: fibrocartilage, slightly movable
Synovial Joints: fluid-filled joint cavity, many are
freely movable joints. Classified according to degree of movement &
shape
1. Nonaxial → plane joint
2. Uniaxial → hinge joint or pivot joint
3. Biaxial → condyloid joint or saddle joint
4. Multiaxial → ball & socket joint
Nonaxial movement: gliding doesn’t involve rotation around an ais e)
intercarpal joint at wrist
Uniaxial movement: movement around single axis
Biaxial Movement: movement around two axes
Multiaxial Movement: movement around multiple axes
Pubic Symphysis
IV Discs
Joint b/w 1st rib
and sternum
Hinge Joint ex) elbow
Pivot Joint ex) proximal radioulnar joint → pronation and supination
Condyloid joint ex) MCP jt at finger
Saddle joint ex) carpo-MC jt at thumb
Ball and Socket joint ex) shoulder
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Anatomical position: anatomical terminology refers to this position. Anatomical planes: pass through the body which provide frame of reference in. Directional terminology: right/left cadaver specific, not the viewers left and right, anterior (ventral)/posterior (dorsal, superior (cranial)/inferior (caudal, medial/lateral, proximal/distal. Uperfi(cid:272)ial fas(cid:272)ia (cid:894)hypodermis (cid:862)(cid:271)elow the dermis(cid:863)(cid:895: contains adipose, fat storage, passageway for nerves and blood vessels. Deep fascia: dense regular connective tissue, creates compartments surrounding individual and groups of muscles and large vessels & nerves, reduces friction during muscle contractions. These are sites where two or more bones meet. They provide stability, and/or mobility to the skeleton. Classified (cid:271)(cid:455) either fun(cid:272)tion or stru(cid:272)ture : functional: immovable, slightly moveable, freely movable, structural: fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial. Fibrous joints: connected by dense regular connective tissue, lack a joint cavity: sutures b/w skull bones, immovable, syndesmoses: connected by ligaments, movement range depends on length, gomphoses: peg-in-socket joint for root of tooth.
