PHYS 101 Chapter Notes - Chapter 7: Elastic Collision, Inelastic Collision, Isolated System
Document Summary
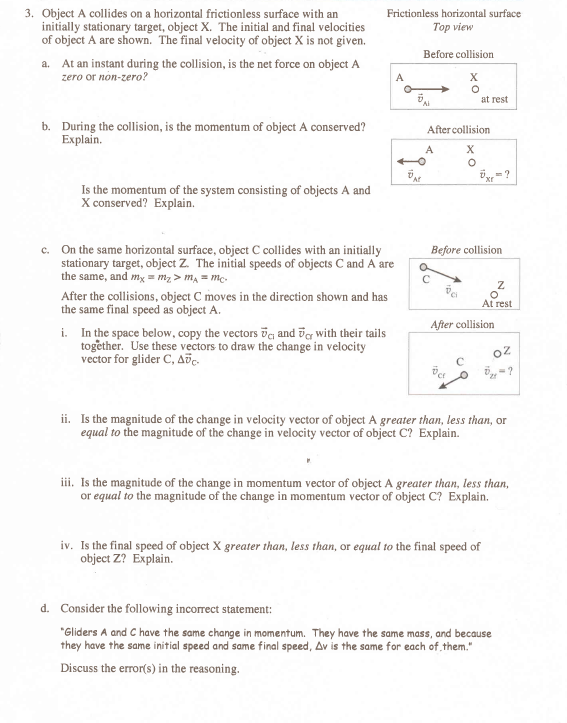
Linear momentum: product of the objects mass and velocity. P = mv: p = momentum (vector), kg m/s, v = velocity, m = mass. The more momentum an object has, the harder it is to stop it. Requires greater or equal opposite force to stop the object with momentum. The rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force applied to it. If no net external force acts on a system, total momentum of system is a conserved. Case with ball collision: m1v1 + m2v2 = m1"v1" + m2"v2", momentum before collision = momentum after collision. Falling rock doesn"t conserve momentum because force of gravity (external force) changes rock"s momentum. If earth is part of system (force of gravity) then total momentum between rock & earth are conserved. During collision, force from 2 objects spikes up from 0 at moment of contact (large force in short time)