MATH 1P66 Lecture Notes - Lecture 2: Idempotence
MATH 1P66 verified notes
2/25View all
Document Summary
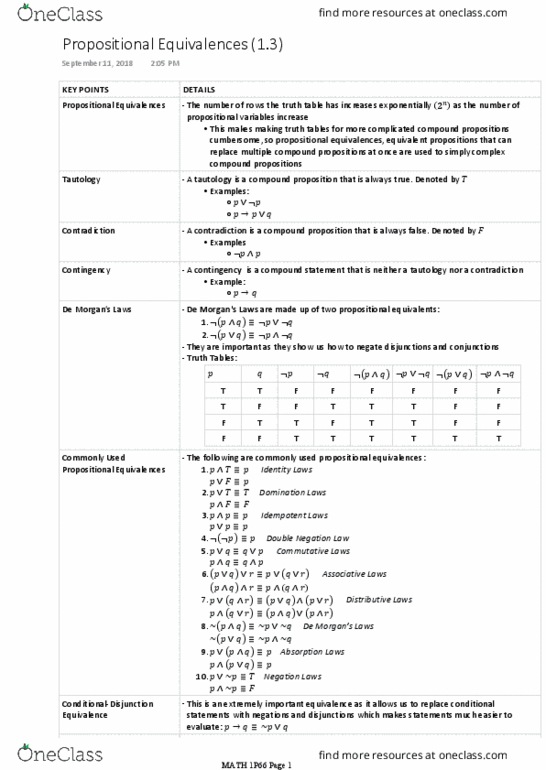
This makes making truth tables for more complicated compound propositions cumbersome, so propositional equivalences, equivalent propositions that can replace multiple compound propositions at once are used to simply complex compound propositions. The number of rows the truth table has increases exponentially as the number of. A tautology is a compound proposition that is always true. A contradiction is a compound proposition that is always false. A contingency is a compound statement that is neither a tautology nor a contradiction. De morgan"s laws are made up of two propositional equivalents: They are important as they show us how to negate disjunctions and conjunctions. Identity laws: domination laws, idempotent laws, double negation law, commutative laws, associative laws. Distributive laws: de morgan"s laws, absorption laws, negation laws evaluate: This is an extremely important equivalence as it allows us to replace conditional statements with negations and disjunctions which makes statements much easier to.