ECON 201 Lecture Notes - Lecture 20: Predatory Pricing, Natural Monopoly, Profit Maximization
ECON 201 verified notes
20/25View all

ECON 201 – Lecture 20 (CHAPTER 10) part 1: Monopoly
(Monday 13/11 week 11)
Keyterms:
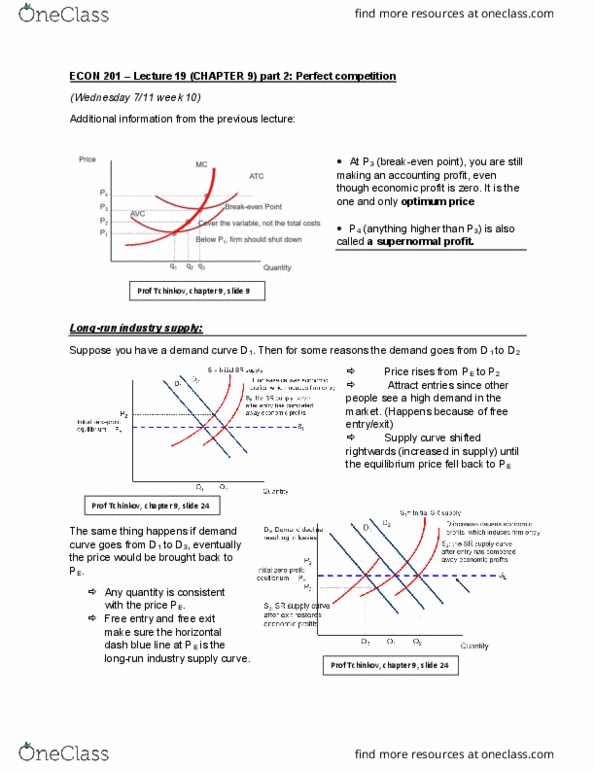
• Natural monopoly: it’s hard for a new
entrance to enter the market and
compete with existing one. As level of
output (Q) ↑, AC (average cost) ↓
=> Increasing return to scale.
Example: Hydro Quebec.
• National policy: Policies that Government lays
down to prevent entries and protect domestic
industry.
Example: Air Canada as the only business within Canada travel.
• Barriers to entry: various ways through which no other business can enter the market:
- Patents: the government grants a legal monopoly to a company to sell in a period of
time. => incentive to invest and create a new good in the first place (others cannot jump
in and copy)
- Predatory pricing: set product/service at a very low price => drive competitors out of
the market
- Lobbying government: protect economic share of the incomer
- Excess production capacity: prevent entry
- Network goods: Example: Facebook: even google cannot compete with Facebook so
they have to shut Google+ down. But nothing can compete with Google in terms of a
search engine.
Consumers don’t like monopoly because there is no competition => they cannot compare which
business sells with better prices for them.
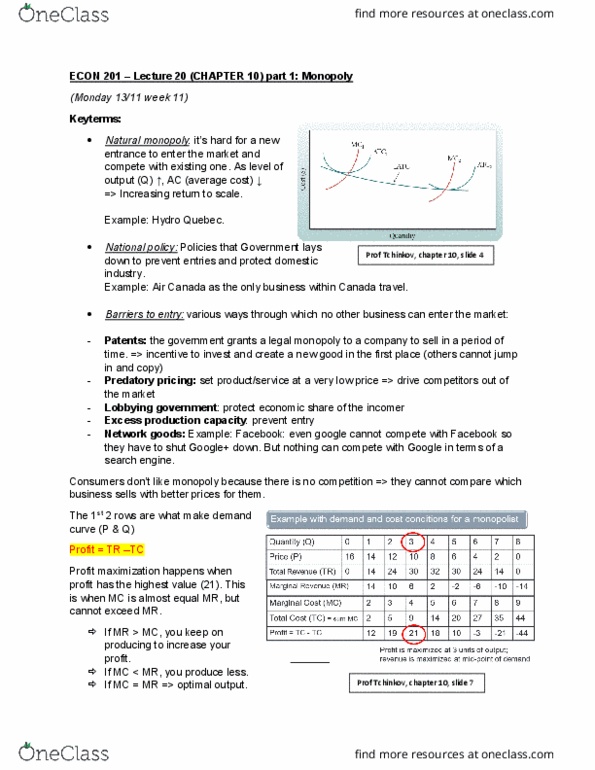
The 1st 2 rows are what make demand
curve (P & Q)
Profit = TR –TC
Profit maximization happens when
profit has the highest value (21). This
is when MC is almost equal MR, but
cannot exceed MR.
If MR > MC, you keep on
producing to increase your
profit.
If MC < MR, you produce less.
If MC = MR => optimal output.
Prof Tchinkov, chapter 10, slide 4
Prof Tchinkov, chapter 10, slide 7
Document Summary
Econ 201 lecture 20 (chapter 10) part 1: monopoly (monday 13/11 week 11) Keyterms: natural monopoly: it"s hard for a new entrance to enter the market and compete with existing one. As level of output (q) , ac (average cost) . Example: hydro quebec: national policy: policies that government lays down to prevent entries and protect domestic industry. Example: air canada as the only business within canada travel. Prof tchinkov, chapter 10, slide 4: barriers to entry: various ways through which no other business can enter the market: Patents: the government grants a legal monopoly to a company to sell in a period of time. => incentive to invest and create a new good in the first place (others cannot jump in and copy) Predatory pricing: set product/service at a very low price => drive competitors out of the market. Lobbying government: protect economic share of the incomer.