PSYC 100 Lecture Notes - Lecture 20: Long-Term Memory, Henry Molaison, Synaptic Plasticity
PSYC 100 verified notes
20/26View all
Document Summary
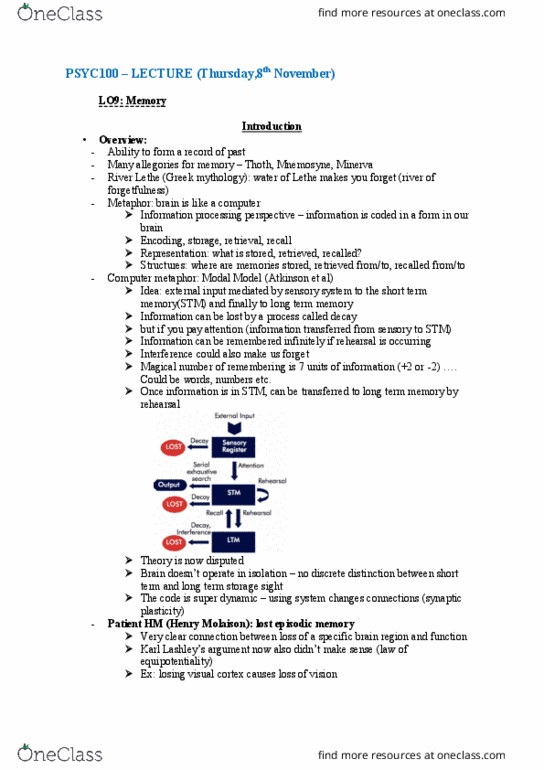
Ability to form a record of past. Many allegories for memory thoth, mnemosyne, minerva. River lethe (greek mythology): water of lethe makes you forget (river of forgetfulness) Information processing perspective information is coded in a form in our brain. Structures: where are memories stored, retrieved from/to, recalled from/to. Computer metaphor: modal model (atkinson et al) Idea: external input mediated by sensory system to the short term memory(stm) and finally to long term memory. Information can be lost by a process called decay. But if you pay attention (information transferred from sensory to stm) Information can be remembered infinitely if rehearsal is occurring. Magical number of remembering is 7 units of information (+2 or -2) . Once information is in stm, can be transferred to long term memory by rehearsal. Brain doesn"t operate in isolation no discrete distinction between short term and long term storage sight. The code is super dynamic using system changes connections (synaptic plasticity)