CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 34: Logical Biconditional, Complex Instruction Set Computing, Truth Table

CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 33: Complex Instruction Set Computing, Logical Connective, Truth Table
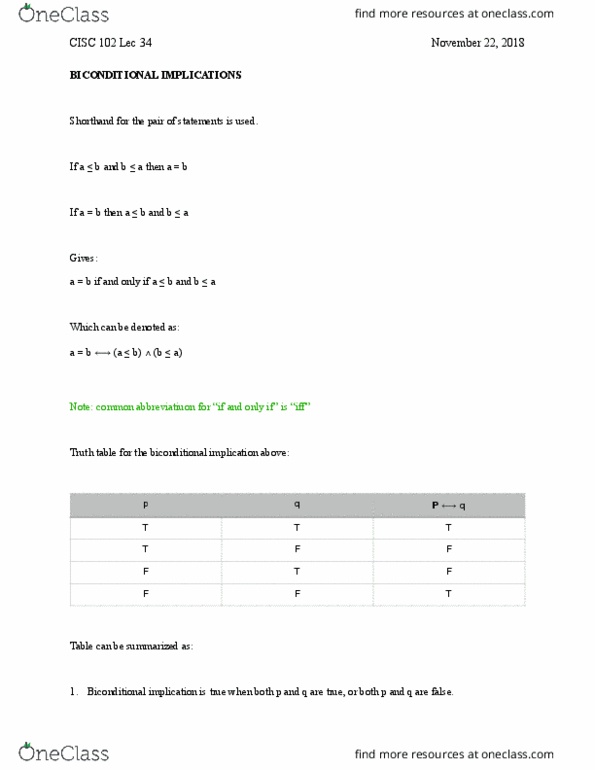
CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 34: Logical Biconditional, Complex Instruction Set Computing, Truth Table

CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 35: Logical Consequence, Complex Instruction Set Computing
Document Summary
Get access


Related Documents
Related Questions
NEED HELP PLEASE. CAN YOU PLEASE DO IT ALL NOT JUST ANSWER ONE.
MY ANIMALS ARE: HUMAN, KANGAROO, RHESUS MONKEY, BULLFROG, LAMPREY, SNAPPING TURTLE, TUNA, AND EARTHWORM
Step 3: Cytochrome c Analysis
Scientists have found that almost all living organisms have a gene that codes for a protein called Cytochrome c. This chart lists the amino acids found in the Cytochrome c protein of some of the organisms on your cladogram.
Note: not all the organisms you used will be in the chart; as such, you can focus this analysis on the animals that are in the chart. If you only chose three animals that are in the chart, you should probably extend your amino acid analysis to include a couple animals that arenât on your cladogram.
You will use the data provided in this chart to compare and analyze the amino acid sequences for Cytochrome c among these organisms. Be sure that your comparison considers the entire amino acid sequence, through amino acid 112, and not just the first lines of the chart. Once you have compared the sequences, you will write a discussion about your findings.
Amino Acid Sequences in Cytochome-C Proteins
1-30
| Amino Acid Position Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| Human, Chimpanzee | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | I | M | K | C | S | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Rhesus Monkey | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | I | M | K | C | S | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Horse | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Pig, Cow, Sheep | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Dog | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Gray Whale | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Rabbit | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Kangaroo | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Penguin | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | I | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | S | O | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Snapping Turtle | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | K |
| Bullfrog | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | E | K | G | K | K | I | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | C | E | K |
| Tuna | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | G | D | V | A | K | G | K | K | T | F | V | Q | K | C | A | Q | C | H | T | V | E | N |
31-60
| Amino Acid Position Number | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| Human, Chimpanzee | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | P | G | Y | S | Y | T | A | A | N |
| Rhesus Monkey | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | P | G | Y | S | Y | T | A | A | N |
| Horse | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | P | G | F | T | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Pig, Cow, Sheep | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | P | G | F | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Dog | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | P | G | F | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Gray Whale | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | V | G | F | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Rabbit | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | V | G | F | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Kangaroo | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | N | G | I | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | P | G | F | T | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Penguin | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | I | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | E | G | F | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Snapping Turtle | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | N | G | L | I | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | E | G | F | S | Y | T | E | A | N |
| Rattlesnake | G | G | K | H | K | T | G | P | N | L | H | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | V | G | Y | S | Y | T | A | A | N |
| Bullfrog | G | G | K | H | K | V | G | P | N | L | Y | G | L | I | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | A | G | F | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
| Tuna | G | G | K | H | K | V | G | P | N | L | W | G | L | F | G | R | K | T | G | Q | A | E | G | Y | S | Y | T | D | A | N |
61-90
| Amino Acid Position Number | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 38 | 69 | 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 |
| Human, Chimpanzee | K | N | K | G | I | I | W | G | E | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Rhesus Monkey | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Horse | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | K | E | E | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Pig, Cow, Sheep | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | E | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Dog | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | E | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Gray Whale | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | E | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Rabbit | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Kangaroo | K | N | K | G | I | I | W | G | E | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Penguin | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Snapping Turtle | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | E | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Rattlesnake | K | N | K | G | I | I | W | G | D | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | V | F |
| Bullfrog | K | N | K | G | I | T | W | G | E | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
| Tuna | K | S | K | G | I | V | W | N | N | D | T | L | M | E | Y | L | E | N | P | K | K | Y | I | P | G | T | K | M | I | F |
91-112
| Amino Acid Position Number | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 | 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 | 110 | 111 | 112 |
| Human, Chimpanzee | V | G | I | K | K | K | E | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Rhesus Monkey | V | G | I | K | K | K | E | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Horse | A | G | I | K | K | K | T | E | R | E | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Common Zebra | A | G | I | K | K | K | T | E | R | E | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Pig, Cow, Sheep | A | G | I | K | K | K | G | E | R | E | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Dog | A | G | I | K | K | T | G | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | K | E |
| Gray Whale | A | G | I | K | K | K | G | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Rabbit | A | G | I | K | K | K | D | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Kangaroo | A | G | I | K | K | K | G | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | K | A | T | N | E |
| Penguin | A | G | I | K | K | K | S | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | D | A | T | S | K |
| Snapping Turtle | A | G | I | K | K | K | A | E | R | A | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | D | A | T | S | K |
| Rattlesnake | T | G | L | K | K | K | K | E | R | T | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | E | A | T | A | K |
| Bullfrog | A | G | I | K | K | K | G | E | R | Q | D | L | I | A | Y | L | K | S | A | C | S | K |
| Tuna | A | G | I | K | K | K | G | E | R | Q | D | L | V | A | Y | L | K | S | A | T | S | - |
More information:
Cytochrome c is a protein used in cellular respiration by most eukaryotes, which is why it's a very common protein to use for comparisons. You don't need to know anything about cellular respiration or the protein itself to do this analysis; just remember that a protein is a specific chain of amino acids.
Which amino acids are found, and the order in which they're found (their sequence), determine the shape, structure, and function of the protein. Also remember that an amino acid sequence is directly determined by the DNA sequence, so similarities in one also indicate similarities in the other.
Please note that the entire sequence of 112 amino acids represents one protein, and this sequence data is all one chart, not four. As such, your analysis should consider the sequence as a whole, and not amino acids 1 â 30, then amino acids 31 â 60, etc.
Be careful not to read too much into the differences you find. Since this analysis only looks at one protein, you will not be able to connect differences here to specific differences in traits between organisms. In other words, it might be that all animals with a placenta have a âVâ at a particular location, while animals without a placenta have either a âCâ or a âK.â That similarity helps us confirm that those animals with a placenta are more closely related to each other than to the others, but the âVâ does not code for the placenta, nor is it related to that particular trait at all.
How to Analyze the Data
While you analyze the data that you are given to identify similarities and differences, be sure to use specific data to draw your comparisons, hypotheses, and discussions from. It is especially helpful to quantitatively compare data. A good way to do this, or at least to start, is to pick one species as a starting point or âbaselineâ and then compare the amount of differences between that and each other species. Be careful, though, about the conclusions you draw â if species B and C each have 5 differences from species A, then they could have anywhere from 0 to 10 differences with each other!
Once youâve compared each animal to a baseline animal, you should also compare other pairs of species so that you can discuss their specific relationships. If you only have a few animals with data to analyze in part C, you could simply make this comparison for every pair. If you have 6 or 7 animals, then you could pick just a few pairs to compare.
There are other legitimate ways to form quantitative data â for instance, you could focus on specific locations where most animals have the same amino acid, but some are different. These types of analysis tend to be harder to interpret, though. If you choose to use them, I suggest that you still complete at least some of the above types of analysis as well.
The discussion topics that I'm looking for are:
Use the chart to compare the amino acid sequences for the organisms. Do this in a way that lets you obtain quantitative (numerical) data; see above for suggestions.
Hypothesize about how closely related the different organisms are, based on the amino acid data in the chart.
In particular, focus on organisms that are also found on your phylogenetic tree, but you may choose to discuss others, too. That would be especially helpful if you used only three or four of the organisms that are also in the chart, or if one or more organisms that you did not include in your tree jump out at you as being especially similar or especially different from the ones you did include.
This does not need to be in the form of a formal hypothesis; that is, you do not need to put this in âif/then/becauseâ form.
Because âhow closely relatedâ can be interpreted in many ways, itâs often helpful to put this in relative terms: âAnimal D is the closest relative to Animal A.â âAnimals C and B are more closely related to each other than either one is to Animal D.â
Discuss how this analysis compares to the relationships that were shown on your phylogenetic tree.
To start, does the Cytochrome c data agree or disagree with the relationships shown on the tree?
Remember that "discuss" means more than simply identifying whether the relationships are the same or different as what is shown. You can also suggest why they're likely the same, or what possible differences could imply, if anything. See the note at the end of âMore Informationâ above â donât read TOO MUCH into any one piece of data!
If your amino acid analysis included animals that werenât on your cladogram, you could use your amino acid data to speculate where they likely âfitâ on the cladogram.
The phrase âcommon ancestorâ should show up somewhere in this discussion.
Please be aware that Step 3 should be written as a short essay, not a list or set of questions and answers. You may include a chart or table for the quantitative data you identified, but the key findings should also be written in sentence form. Once youâve finished writing this, please proofread for spelling, grammar, and writing clarity.
Step 3 should be a sizeable portion of this portfolio. I expect that your analysis should be about 250 â 400 words long in order to thoroughly analyze the data and discuss the questions.


