BUEC 232 Lecture Notes - Lecture 7: Conditional Probability, University Of Florida, Random Variable
BUEC 232 verified notes
7/10View all
Document Summary
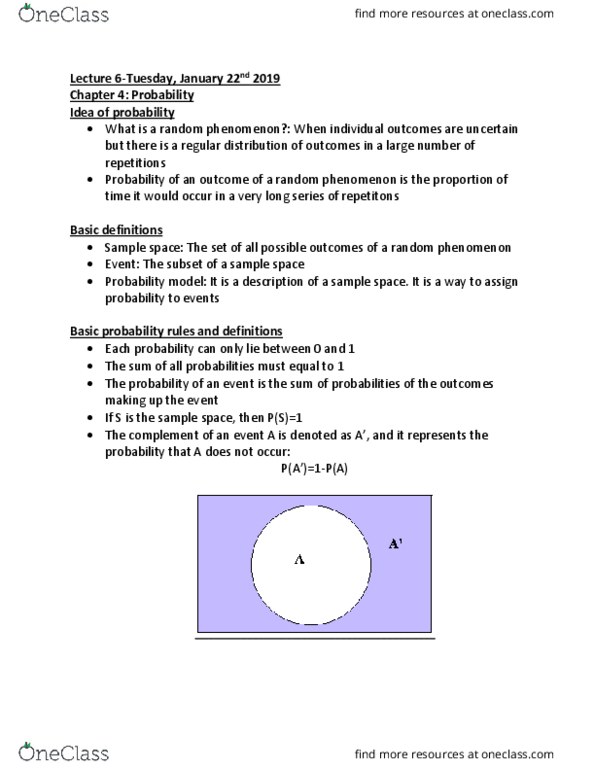
The outcome of each die is in no way affected by the other, they are completely independent. Unions: two events a and b are given. The union of these two events is written as: A u b: an important formula for unions is: p(a u b)=p(a) + p(b) - p(a and b). This rule is referred to as the addition rule: example of unions: we have a class of 100mba students. Accounting (a), 15 take finance(f) and 10 take both. : in this case, at least on subject refers to. Therefore, it is just p(a) + p(f) - p(a and f) which is 25+15-10=30. Conditional probability: conditional probability that x occurs given that y occurs is p(x|y, we can define conditional probabilities in terms of unconditional probabilities, p(b|a)= p(b and a)/p(a, p(a and b) can also be written as: p(b)*p(a|b)