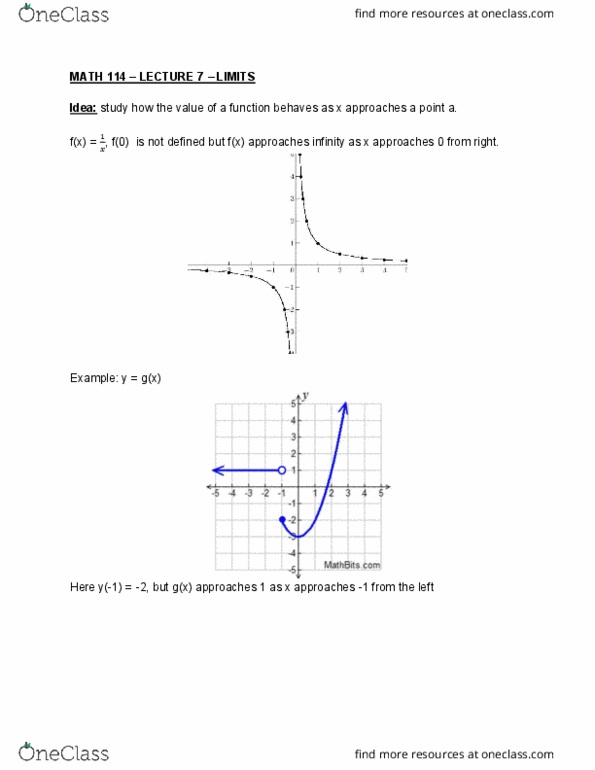
1. 0/6 points LarCalc11 13.1.010. [3864 VIA Evaluate the function at the given values of the independent variables. Simplify the results. fx, y) -4 -x2 - 4y2 (a) ro, 0) for (c) f2, 3) (e) x, o Cal 2. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.1.019.MI. [386 Evaluate the function at the given values of the independent variables. Simplify the results. x, y)- 6x y2 (a) fix + ax, y)-f(x, y) Ay
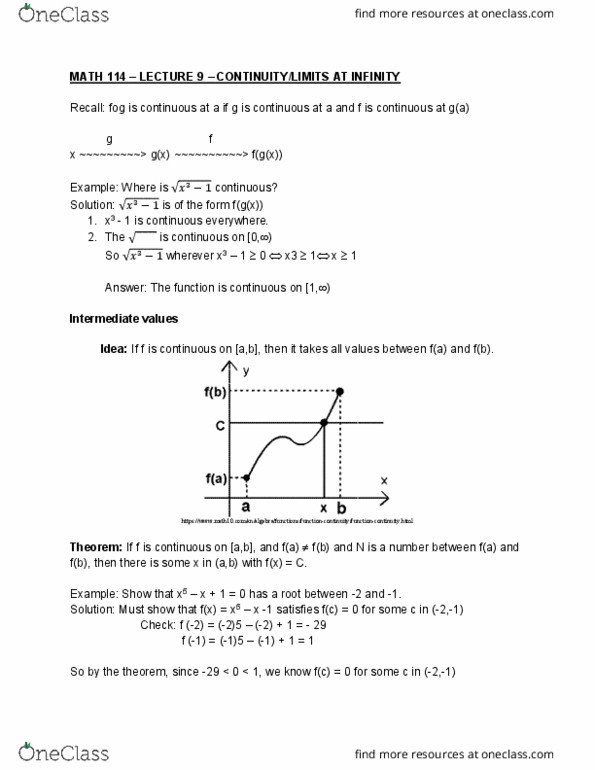
3. 1 points LarCalc11 13.2 Find the indicated limit by using the limits limfx, y) 2 and im g(x, y)--4 lim 4. O/1 points LarCalci1 13 2 Find the indicated limit by using the limits lim x, y) 3 and lim (x, y) g(x, y)--5 (a, b) lim x, Y) (x, y) (a, b) g(x, y) 5. y1 points LarCalc11 13.3 Explain whether or not the Quotient Rule should be used to find the partial derivative. Do not differentiate. ay x2 51 O Yes, the function is a quotient. O No, y only occurs in the numerator. 6. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.3 Find both first partial derivatives oz 7. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.3 Find both first partial derivatives. hx, y) ex+y) h(x, y)
8. /2 points LarCalc11 13.3.031 Find both first partial derivatives. az dx az ay 9. /1 points LarCalc11 13.4.003. Find the total differential. z 3xSy10 dz 10. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.5.012 Consider the following. (a) Find dw/dt using the appropriate Chain Rule. dw dt (b) Find dw/dt by converting w to a function of t before differentiating. dw dt 11. 0/1 points LarCalc11 13.6.008. Find the directional derivative of the function at P in the direction of v. rx, y) = x3-y3, Rio, 9), v-V2 (1+j)
12. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.7.017 (a) Find an equation of the tangent plane to the surface at the given point. x+y+z=9, (2, 5, 2) (b) Find a set of symmetric equations for the normal line to the surface at the given point. ox -2y -5-z-2 13. /3 points LarCalc11 13.8.025 Use a computer algebra system to graph the surface and locate any relative extrema and saddle points. (If an an not exist, enter DNE.) -8x x2 y21 relative minimum (x, y, z) - relative maximum (x, y, z) saddle point 14. 0/1 points LarCalci1 13.10.027 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the minimum distance from the curve or surface to the indicated point. Surface Point Plane: x yz 1 (7,1,1)
Show transcribed image text 1. 0/6 points LarCalc11 13.1.010. [3864 VIA Evaluate the function at the given values of the independent variables. Simplify the results. fx, y) -4 -x2 - 4y2 (a) ro, 0) for (c) f2, 3) (e) x, o Cal 2. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.1.019.MI. [386 Evaluate the function at the given values of the independent variables. Simplify the results. x, y)- 6x y2 (a) fix + ax, y)-f(x, y) Ay
3. 1 points LarCalc11 13.2 Find the indicated limit by using the limits limfx, y) 2 and im g(x, y)--4 lim 4. O/1 points LarCalci1 13 2 Find the indicated limit by using the limits lim x, y) 3 and lim (x, y) g(x, y)--5 (a, b) lim x, Y) (x, y) (a, b) g(x, y) 5. y1 points LarCalc11 13.3 Explain whether or not the Quotient Rule should be used to find the partial derivative. Do not differentiate. ay x2 51 O Yes, the function is a quotient. O No, y only occurs in the numerator. 6. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.3 Find both first partial derivatives oz 7. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.3 Find both first partial derivatives. hx, y) ex+y) h(x, y)
8. /2 points LarCalc11 13.3.031 Find both first partial derivatives. az dx az ay 9. /1 points LarCalc11 13.4.003. Find the total differential. z 3xSy10 dz 10. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.5.012 Consider the following. (a) Find dw/dt using the appropriate Chain Rule. dw dt (b) Find dw/dt by converting w to a function of t before differentiating. dw dt 11. 0/1 points LarCalc11 13.6.008. Find the directional derivative of the function at P in the direction of v. rx, y) = x3-y3, Rio, 9), v-V2 (1+j)
12. 0/2 points LarCalc11 13.7.017 (a) Find an equation of the tangent plane to the surface at the given point. x+y+z=9, (2, 5, 2) (b) Find a set of symmetric equations for the normal line to the surface at the given point. ox -2y -5-z-2 13. /3 points LarCalc11 13.8.025 Use a computer algebra system to graph the surface and locate any relative extrema and saddle points. (If an an not exist, enter DNE.) -8x x2 y21 relative minimum (x, y, z) - relative maximum (x, y, z) saddle point 14. 0/1 points LarCalci1 13.10.027 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the minimum distance from the curve or surface to the indicated point. Surface Point Plane: x yz 1 (7,1,1)