MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 11: Product Rule
MATH114 verified notes
11/28View all
Document Summary
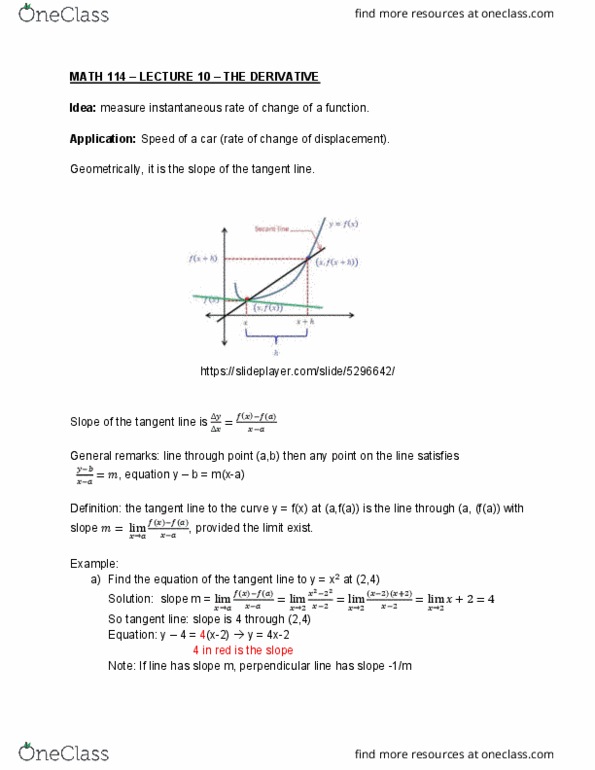
Math 114 lecture 11 the derivative continuation: constant functions f(x) = c f"(x) = lim (cid:2868)(cid:3033)(cid:4666)+ (cid:4667) (cid:3033)(cid:4666)(cid:4667) =(cid:1866) (cid:1853) (cid:2869: power functions f(x) = xn, n is positive. Example: f(x) = x2 f"(x) = 2x f(x) = x3 f"(x) = lim (cid:2868)(cid:4666)+ (cid:4667)(cid:3119) (cid:3119) Theorem: f(x) = xn f"(x) = nx(n-1) for n positive. In fact, this is also valid for negative values of n. Theorem: f(x) = xn f"(x) = nx(n-1) for n = any real number: exponential functions. Definition: the number e is the unique real number such that lim (cid:2868)(cid:3032) (cid:2869) =(cid:883) We separated bx because it is independent of h. So for f(x) = ex, we have f"(0) = 1, so f"(x) = ex f"(0) = ex(1) = ex. If we know f" and g", can we find the derivative of cf, f+g,f-g and f/g: constant multiples (cid:1856)(cid:1856)((cid:1855)(cid:1858)(cid:4666)(cid:4667))=lim (cid:2868)(cid:1858)(cid:4666)+ (cid:4667) (cid:1858)(cid:4666)(cid:4667) Similar process as the sum but the sign changes.