ECON 101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 13: Market Power, Demand Curve, Takers
ECON 101 verified notes
13/13View all
Document Summary
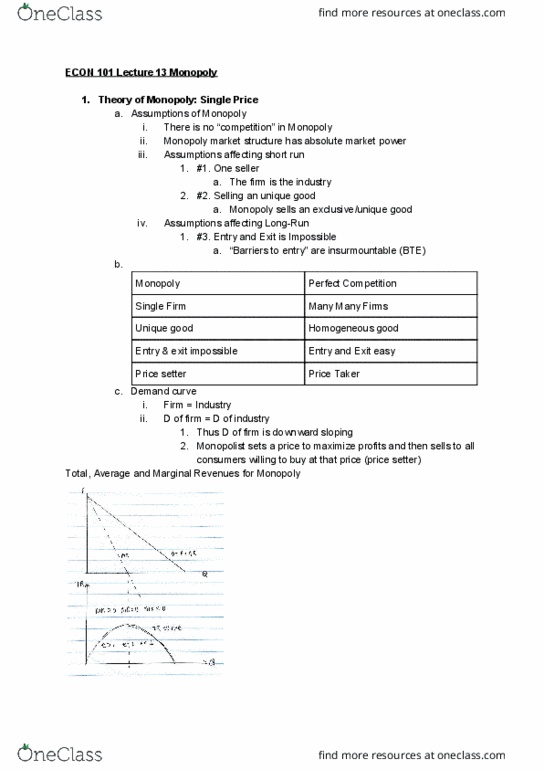
Econ 101 lecture 13 monopoly: theory of monopoly: single price, assumptions of monopoly. There is no competition in monopoly i: monopoly market structure has absolute market power iii. One seller: the firm is the industry, #2. Selling an unique good: monopoly sells an exclusive/unique good iv. Price taker: thus d of firm is downward sloping, monopolist sets a price to maximize profits and then sells to all consumers willing to buy at that price (price setter) Total, average and marginal revenues for monopoly: short run profit maximization, monopoly profits i. ii. iii. Monopoly will not produce where e<1, mr <0, tr decreasing: reason: for the same revenue tr, costs lower at q1 than q2. A profit maximizing monopolist will produce output where it covers its day-to-day expenses. A profit maximizing monopolist will produce output where mr. Rules 2 & 3 are the same for any market structure. Four steps to eternal bliss: mr = mc, to find profit max.