MAT 1302 Lecture Notes - Lecture 19: Linear Map, Triangular Matrix
MAT 1302 verified notes
19/26View all
Document Summary
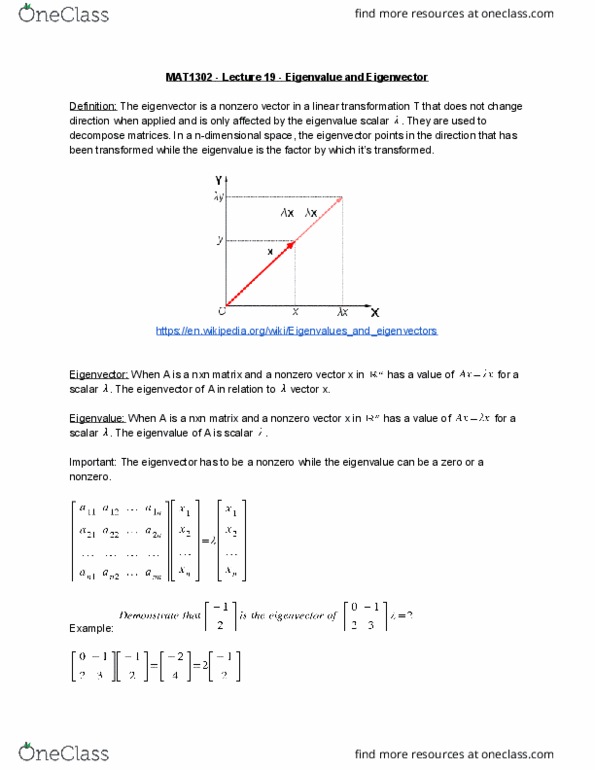
Mat1302 - lecture 19 - eigenvalue and eigenvector. Definition: the eigenvector is a nonzero vector in a linear transformation t that does not change direction when applied and is only affected by the eigenvalue scalar decompose matrices. In a n-dimensional space, the eigenvector points in the direction that has been transformed while the eigenvalue is the factor by which it"s transformed. Eigenvector: when a is a nxn matrix and a nonzero vector x in scalar. Eigenvalue: when a is a nxn matrix and a nonzero vector x in scalar. Important: the eigenvector has to be a nonzero while the eigenvalue can be a zero or a nonzero. The eigenvalue of a is scalar has a value of has a value of for a for a. Example: is an eigenvalue of a if and only if the homogeneous linear system has. Triangular matrix eigenvalue: the eigenvalues are the diagonal entries. formed by a set of vectors x that satisfy.