CHM136H1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 22: Isomerization, Alkene, Stereoisomerism
CHM136H1 verified notes
22/39View all
Document Summary
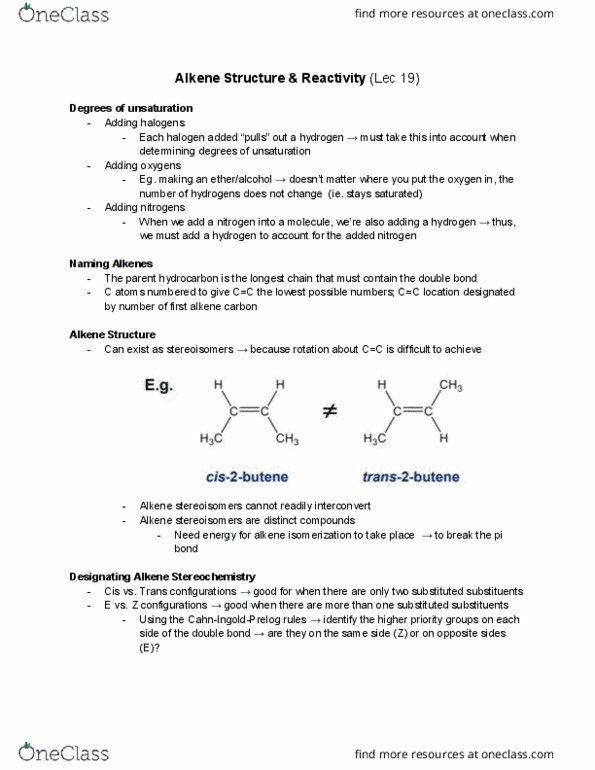
Each halogen added pulls out a hydrogen must take this into account when determining degrees of unsaturation. Eg. making an ether/alcohol doesn"t matter where you put the oxygen in, the number of hydrogens does not change (ie. stays saturated) When we add a nitrogen into a molecule, we"re also adding a hydrogen thus, we must add a hydrogen to account for the added nitrogen. The parent hydrocarbon is the longest chain that must contain the double bond. C atoms numbered to give c=c the lowest possible numbers; c=c location designated by number of first alkene carbon. Can exist as stereoisomers because rotation about c=c is difficult to achieve. Need energy for alkene isomerization to take place to break the pi bond. Cis vs. trans configurations good for when there are only two substituted substituents. E vs. z configurations good when there are more than one substituted substituents.