EECS 1520 Lecture Notes - Lecture 6: Positional Notation, Natural Number, 5,6,7,8
EECS 1520 verified notes
6/14View all
Document Summary
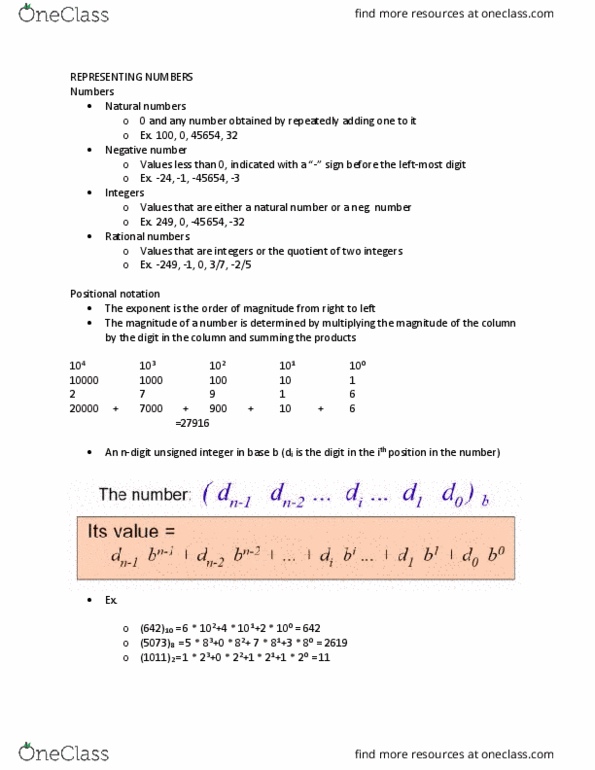
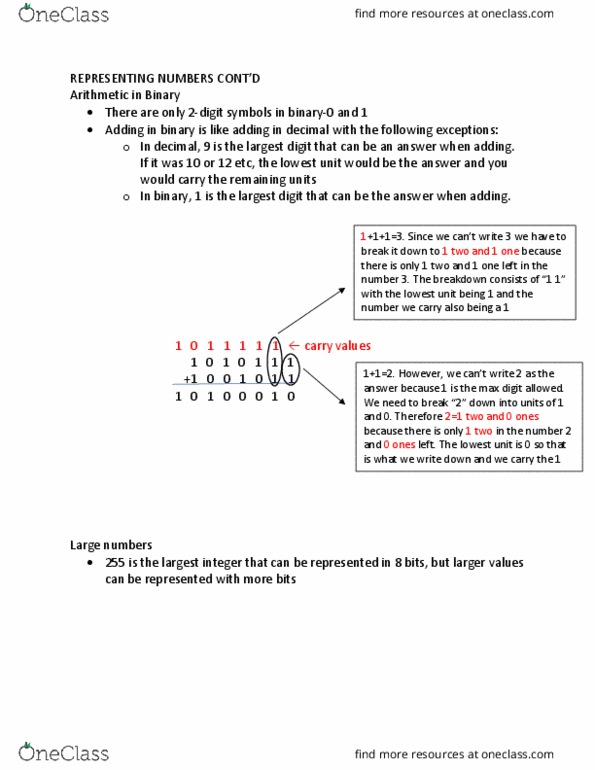
Numbers: natural numbers, 0 and any number obtained by repeatedly adding one to it, ex. 100, 0, 45654, 32: negative number, values less than 0, indi(cid:272)ated with a (cid:862)-(cid:863) sign (cid:271)efore the left-most digit, ex. Integers: values that are either a natural number or a neg. number, ex. 249, 0, -45654, -32: rational numbers, values that are integers or the quotient of two integers, ex. Positional notation: the exponent is the order of magnitude from right to left, the magnitude of a number is determined by multiplying the magnitude of the column by the digit in the column and summing the products. Non- decimal number systems: decimal has a base of 10 and has 10 digit symbols, ex. The largest decimal value that can be expressed in 8 bits. Representation for 0, making 256 (28) combinations of 0 and 1 in 8 bits.