EECS 1520 Lecture 7: REPRESENTING NUMBERS 2
211 views2 pages
Verified Note
12 Oct 2018
School
Course
Professor
EECS 1520 verified notes
7/14View all
Document Summary
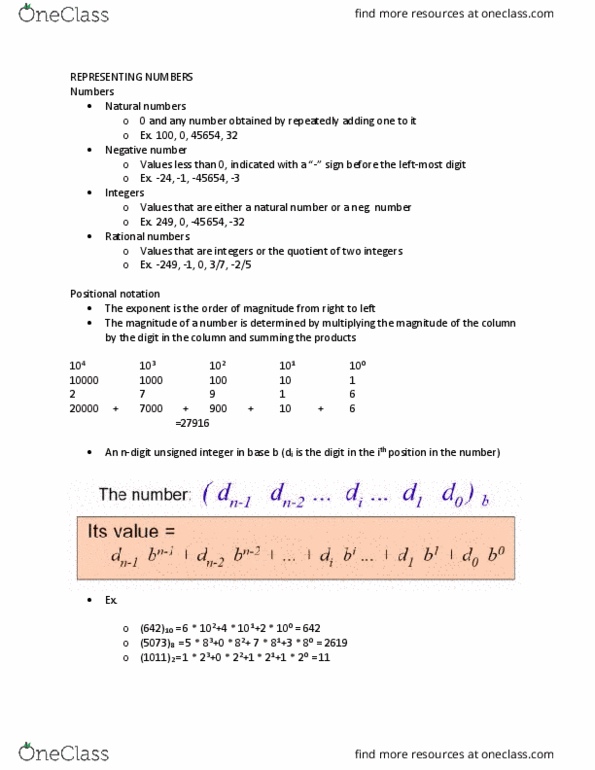
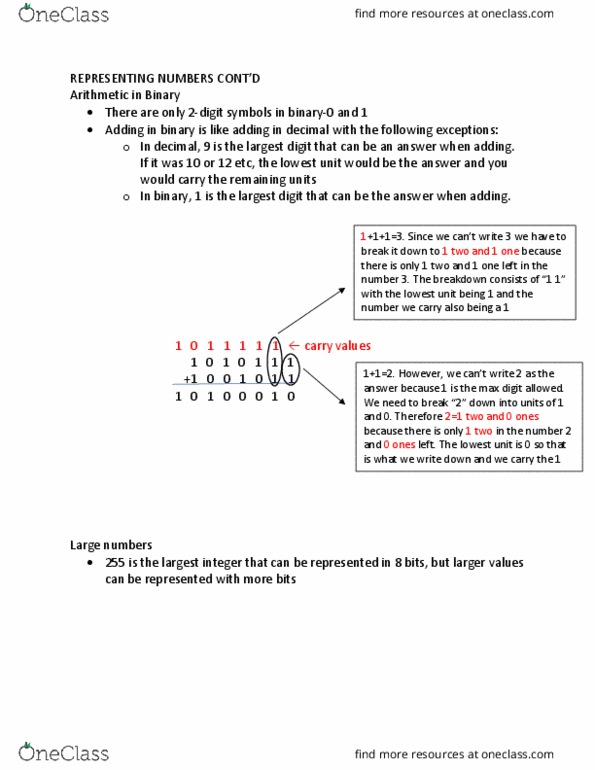
Arithmetic in binary: there are only 2-digit symbols in binary-0 and 1, adding in binary is like adding in decimal with the following exceptions, in decimal, 9 is the largest digit that can be an answer when adding. If it was 10 or 12 etc, the lowest unit would be the answer and you would carry the remaining units: in binary, 1 is the largest digit that can be the answer when adding. Sin(cid:272)e (cid:449)e (cid:272)a(cid:374)"t (cid:449)rite (cid:1007) (cid:449)e ha(cid:448)e to break it down to 1 two and 1 one because there is only 1 two and 1 one left in the (cid:374)u(cid:373)(cid:271)er (cid:1007). The (cid:271)reakdo(cid:449)(cid:374) (cid:272)o(cid:374)sists of (cid:862)(cid:1005) (cid:1005)(cid:863) with the lowest unit being 1 and the number we carry also being a 1. 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 carry values. Ho(cid:449)e(cid:448)er, (cid:449)e (cid:272)a(cid:374)"t (cid:449)rite (cid:1006) as the answer because 1 is the max digit allowed.
Get access
Grade+20% off
$8 USD/m$10 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
40 Verified Answers
Class+
$8 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
30 Verified Answers