MATH 1300 Lecture Notes - Lecture 20: Difference Quotient
MATH 1300 verified notes
20/39View all
Document Summary
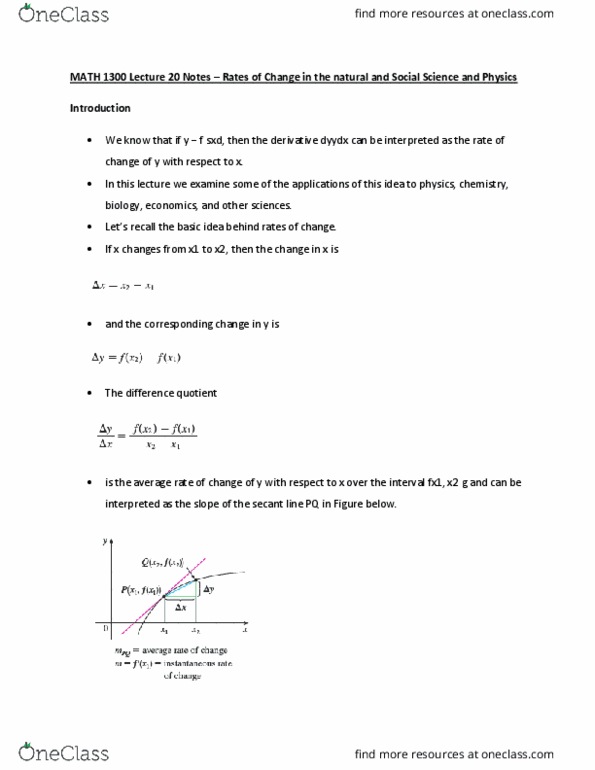
Math 1300 lecture 20 notes rates of change in the natural and social science and physics. Introduction: we k(cid:374)o(cid:449) that if (cid:455) f s(cid:454)d, the(cid:374) the deri(cid:448)ati(cid:448)e d(cid:455)(cid:455)d(cid:454) (cid:272)a(cid:374) (cid:271)e i(cid:374)terpreted as the rate of change of y with respect to x. In this lecture we examine some of the applications of this idea to physics, chemistry, biology, economics, and other sciences: let"s re(cid:272)all the (cid:271)asi(cid:272) idea (cid:271)ehi(cid:374)d rates of (cid:272)ha(cid:374)ge. Its limit as dx l 0 is the derivative f 9sx1d, which can therefore be interpreted as the instantaneous rate of change of y with respect to x or the slope of the tangent line at. If s f std is the positio(cid:374) fu(cid:374)(cid:272)tio(cid:374) of a parti(cid:272)le that is (cid:373)o(cid:448)i(cid:374)g i(cid:374) a straight li(cid:374)e, the(cid:374) 0, that is: this inequality is true when both factors are positive st .