MATH 1231 Lecture Notes - Lecture 2: Oliver Heaviside, Asymptote
MATH 1231 verified notes
2/5View all
Document Summary
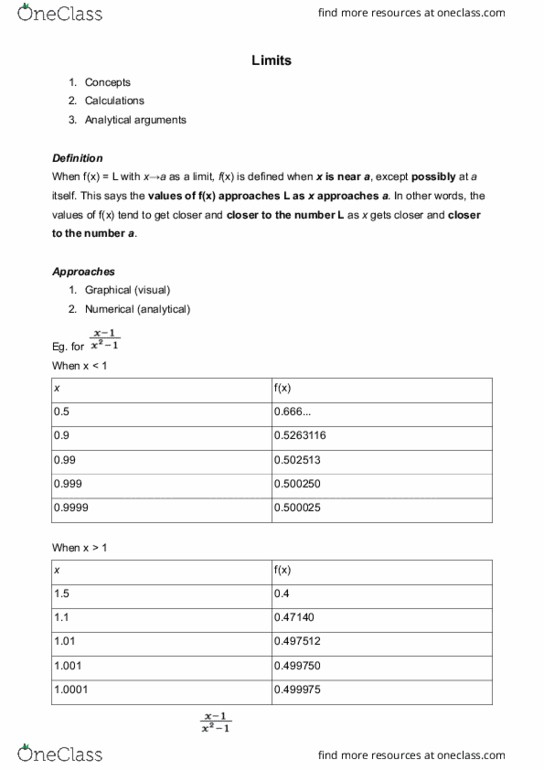
When f(x) = l with x a as a limit, f(x) is defined when x is near a, except possibly at a itself. This says the values of f(x) approaches l as x approaches a. In other words, the values of f(x) tend to get closer and closer to the number l as x gets closer and closer to the number a. One sided limits: heaviside function, h(t) = 0 if t < 0 or h(t) = 1 if t 0. H(t) = ? with limit t 0. H(t) = 0 when limit t 0^ (the sign signifies that t approaches 0 from the left) H(t) = 1 when limit t 0^+ (the + sign signifies that t approaches 0 from the right) H(t) = dne (does not exist) when limit t 0. In general, f(x) = l when limit x a^ or when limit x a^+ f(x) = l x a.