ECON 200 Lecture Notes - Lecture 3: Opportunity Cost, Tax Bracket, Economic Surplus
ECON 200 verified notes
3/20View all
Document Summary
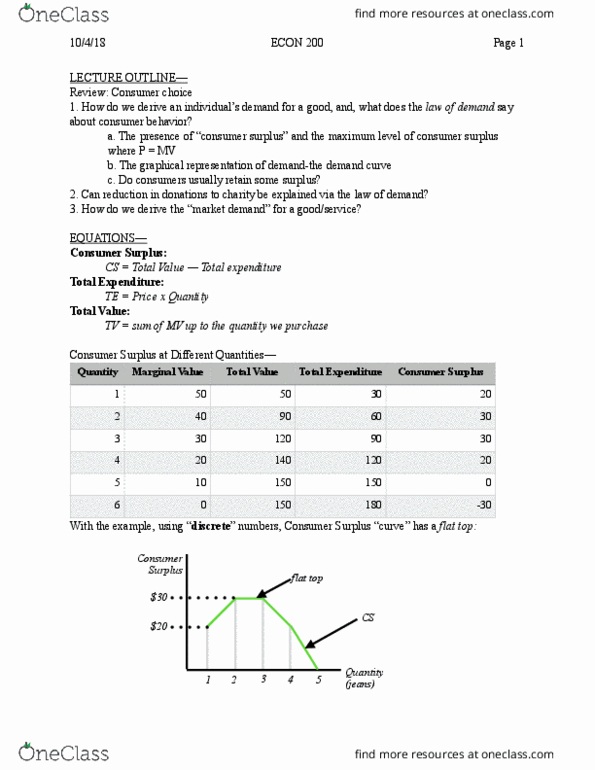
Tv = sum of mv up to the quantity we purchase. With the example, using discrete numbers, consumer surplus curve has a flat top: If the rate of consumption of blue jeans were on a continuous scale: A consumer chooses quantity at q*, such that, at q*, consumer surplus is maximized: Choose a q*, such that, marginal value is equal to price; p = mv: d(cs) = d(tv) d(pxq) = 0 dq dq dq, d(cs) = mv p = 0 dq. Explains regularity of behavior among people who buy goods and services. A demand curve shows the quantities of a good that consumers are willing to buy at different prices; keeping everything else (income of consumers, prices of other goods/ services, laws/regulations, age, location, etc. ) constant. At any given price, consider and sum up the quantities that they are all buying (the consuming market); plug into a graph to identify the demand curve.