CHEM 1A Lecture Notes - Lecture 23: Homonuclear Molecule, Antibonding Molecular Orbital, Noble Gas
CHEM 1A verified notes
23/31View all
Document Summary
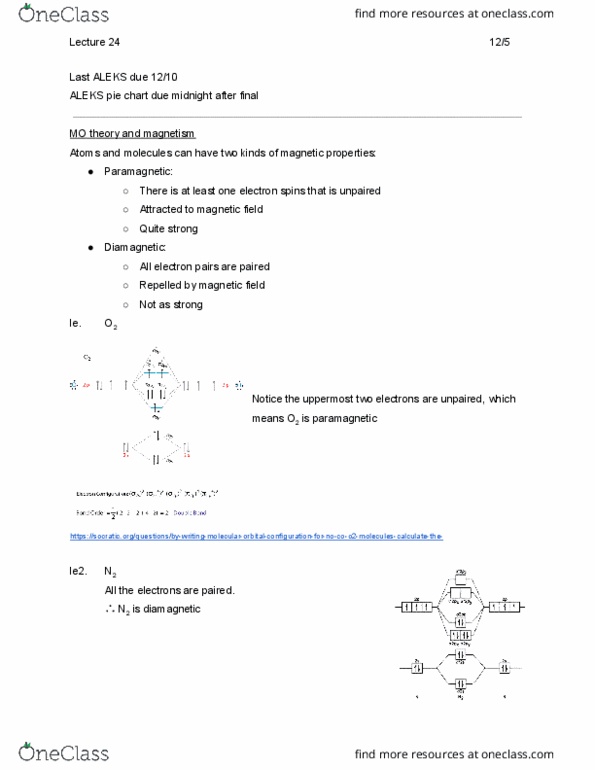
Molecular orbital model bonding in homonuclear diatomic molecules. Now let"s extend the understanding of electrons as wave function from just atoms to molecules. Constructive interference: when two waves are in phase. Destructive interference: when two waves are out of phase. H 2 : for each h atom, the electron is in 1s. Each electron in 1s has wave property, which can be either positive or negative. *note, this sign is specifically due to the wave nature of electrons, not to the electric charge! Therefore, when we add two electrons that are in 1s together, there can be only 2 situations: Bonding orbital is more stable than * antibonding orbital, meaning that it takes less energy for electrons to be in than *. This is illustrated in the energy diagram below. We fill these energy diagrams just like how we would fill it for atoms, filling from the bottom up (lowest energy) and all the other rules.