PHYS 6A Lecture Notes - Lecture 4: Systematic Chaos, Physical Quantity, Pythagorean Theorem
PHYS 6A verified notes
4/20View all
Document Summary
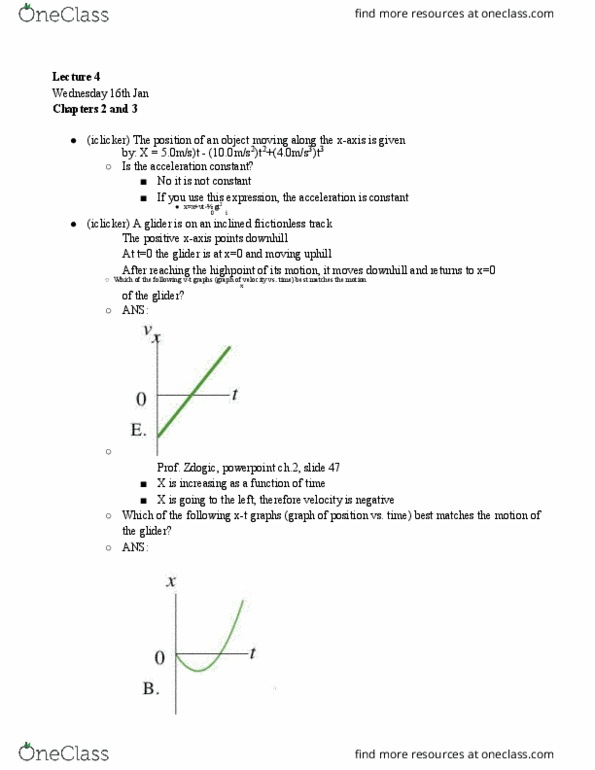
(iclicker) the position of an object moving along the x-axis is given by: x = 5. 0m/s)t - (10. 0m/s2)t2+(4. 0m/s3)t3. If you use this expression, the acceleration is constant. (iclicker) a glider is on an inclined frictionless track. At t=0 the glider is at x=0 and moving uphill. After reaching the highpoint of its motion, it moves downhill and returns to x=0. X is increasing as a function of time. X is going to the left, therefore velocity is negative. Glider is going left, therefore it is negative. The slope"s highest point = change in direction. Constant motion: moving at the same speed in the same direction. Equations that relate position, velocity, and acceleration: vx=v0x+ axt x= x +v 0x t+ a t2 v2 =v2 +2a(x-x ) Scalars: physical quantity with no direction associated. Speed: physically how fast you are going. Vectors: a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Displacement: how far and what direction you traveled.