ECON 310 Lecture Notes - Lecture 5: Nominal Interest Rate, Real Interest Rate, Economic Equilibrium
ECON 310 verified notes
5/27View all
Document Summary
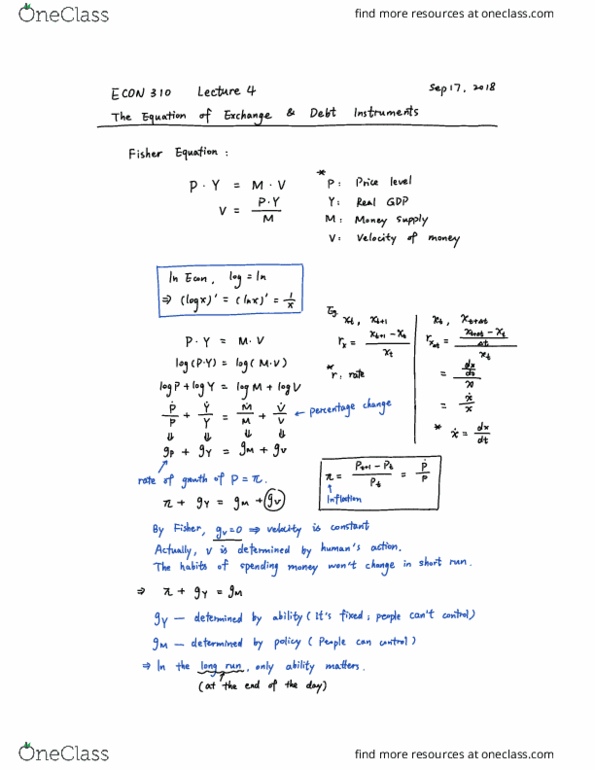
Rate of return=1% p= , 5% and . A bond"s price and yield to maturity are linked by the equation showing its coupon payments, face value (fv) and maturity in n years (1) p= c/(1+i) + c/(1+i)^2 . c/(1+i)^n + fv/(1+i)^n. Coupon and fv do not change, if we know the price in the bond market, we can determine the equilibrium interest. The bond market approach is useful when considering how the factors of demand and supply for bonds affect the interest rate. Price is the only factor to consider when drawing the demand and supply curves for bonds. If the price of bonds changes, we move along the demand curve, changing quantity demanded. Equilibrium price of bonds and quantity of bonds increase as a result of the rightward shift (2) a decrease in wealth will shift the demand curve d1 inward to d2.