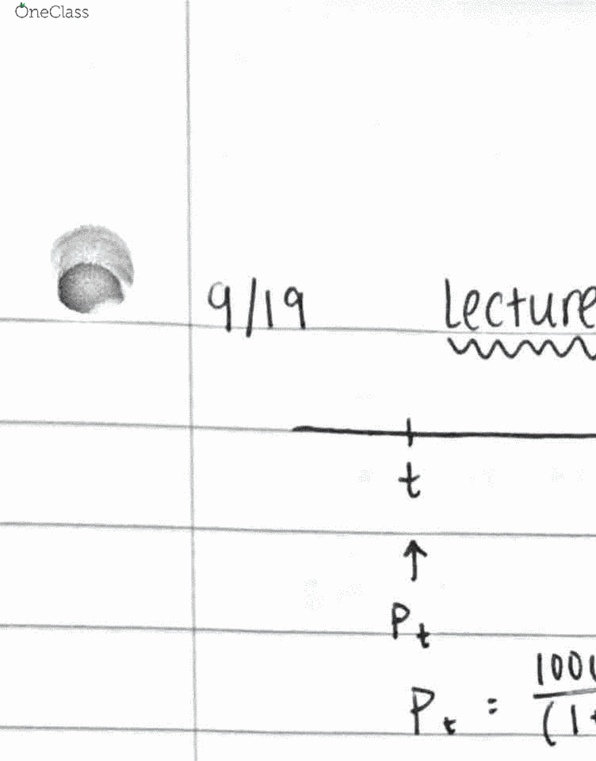
ECON 310 Lecture Notes - Lecture 6: Nominal Interest Rate, Loanable Funds, Real Interest Rate
Document Summary
Get access


Related Documents
Related Questions
QUESTION 11
If the demand for investment loans rises, this could be the result of
| the discovery of new and better roundabout methods of production. | ||
| a lower rate of time preference in society. | ||
| a lower interest rate. | ||
| a higher interest rate. | ||
| a and c |
1 points
QUESTION 12
Which of the following statements is true?
| All persons have a high rate of time preference. | ||
| People with a high rate of time preference are more likely to be borrowers than people with a low rate of time preference. | ||
| People with a high rate of time preference are more likely to be lenders than people with a low rate of time preference. | ||
| A high interest rate is the cause of a high rate of time preference. | ||
| none of the above |
1 points
QUESTION 13
Which of the following statements is true?
| The nominal interest rate is always higher than the real interest rate since the nominal interest rate equals the real interest rate plus the expected inflation rate. | ||
| The nominal interest rate is always lower than the real interest rate since the nominal interest rate equals the real interest rate minus the expected inflation rate. | ||
| The nominal interest rate can equal the real interest rate, but to do so the expected inflation rate must be zero percent. | ||
| It is the nominal interest rate-not the real interest rate-that matters to borrowers. |
1 points
QUESTION 14
If there is an increase in the expected inflation rate, then,
| the supply and demand for loanable funds will decrease. | ||
| the supply and demand for loanable funds will increase. | ||
| the supply of loanable funds will decrease, and the demand for loanable funds will increase. | ||
| the supply of loanable funds will increase, and the demand for loanable funds will decrease. |
1 points
QUESTION 15
If suddenly a 4 percent inflation rate (instead of a zero percent inflation rate) is expected by both suppliers and demanders in the loanable funds market, then
| the demand for loanable funds curve will shift rightward, and the supply of loanable funds curve will shift leftward. | ||
| the demand for loanable funds curve will shift leftward, and the supply of loanable funds curve will shift rightward. | ||
| both the demand for loanable funds curve and the supply of loanable funds curve will shift leftward. | ||
| both the demand for loanable funds curve and the supply of loanable funds curve will shift rightward. |
1.Purchasing power parity implies that
a. the real exchange rate is equal to 1.
b. the law of one price does not hold.
c. inflation rates are equal across countries.
d. the real exchange rate is equal to 0.
e. if the domestic country has low prices, then the domestic currency will depreciate until foreign citizens can buy the same amount of goods as domestic citizens.
2.Which of the following is a prediction from the PPP model of exchange rates?
A. An increase in the US money supply leads to an appreciation of the dollar in the long run.
B. An increase in US production leads to a depreciation of the dollar.
C. An increase in US production will lead to a proportional increase in the inflation rate.
D, An increase in the US money supply leads to a depreciation of the dollar in the long run.
E.An increase in the US interest rates leads to a fall in prices.
3.Relative purchasing power parity predicts that
A.the difference between the inflation rates in the two countries should equal the ratio of the interest rates in the two countries.
B. the difference between the inflation rates in two countries should equal the per cent change in the exchange rate.
C.inflation rates should be equal across countries.
D.the real exchange rate should equal one.
E.relative price levels in the two countries should be equal when expressed in the same currency.
4.Which of the following is NOT a valid explanation for the failure of purchasing power parity?
a. Differences in monetary policies across countries
b. Lack of competition
c. Transportation costs
d. Trade barriers
5.If P represents (the level of) domestic prices, P* represents (the level of) foreign prices and E represents the exchange rate as units of domestic currency per units of foreign currency, then the real exchange rate equals
|
a. EP/P* |
b. P*/EP |
|
C. E/PP* |
d. EP*/P |
|
e. P/P* |
6.The difference between nominal and real interest rates is that
A.Nominal interest rates are measured in terms of a country's output, while real interest rates are measured in monetary terms
B.Nominal interest rates are measured in monetary terms, while real interest rates are measured in terms of a country's output
C.Nominal interest rates can fluctuate, while real interest rates always remain fixed
D.Real interest rates can fluctuate, while nominal interest rates always remain fixed
E.Real interest rates are the same in every country, while nominal interest rates are different for every country
7.Which of the following is predicted to cause the value (or price or cost) of U.S. goods to appreciate relative to the value (or price or cost) of foreign goods in the long run?
a. An increase in the growth rate of U.S. GNP. b. A decrease in the growth rate of U.S. GNP.
c. A decline in the growth rate of the U.S. money supply.
d. An increase in the price of petroleum that reduces world demand for American cars. e. An appreciation of the dollar.
Question 1
The higher the capital utilization rate, the greater the depreciation rate.
| True |
| False |
Question 2
Higher capital utilization rates may raise the user costs of capital because higher utilization rates imply
| operating at inconvenient times. |
| paying overtime to employees operating the machines. |
| operating when complementary services like transporters are unavailable or more expensive. |
| All of the above. |
Question 3
If the rental price of capital increase, the capital utilization rate
| increases. |
| decreases. |
| remains the same. |
| depends on whether the substitution rate is greater than the income effect |
Question 4
The vacancy rate in the labor market is
| the number of job openings divided by the number of unemployed people in the labor force. |
| the number of job openings divided by the number of workers in the labor force. |
| the ratio of open jobs to filled jobs. |
| the ratio of open jobs to the total number of jobs that employers want occupied. |
Question 5
Unemployment can exist in a market clearing model if it takes some search time for workers to find jobs.
| True |
| False |
Question 6
A decrease in workersâ effective real incomes while they are unemployed will
| lower the job finding rate and raise the expected duration of unemployment. |
| lower the job finding rate and the expected duration of unemployment. |
| raise the job finding rate and lower the expected duration of unemployment. |
| raise the job finding rate and the expected duration of unemployment. |
Question 7
In the Barro model, the natural rate of unemployment is
| positively related to the job separations rate. |
| zero. |
| fixed. |
| positively related to the job finding rate. |
Question 8
If the interest rate increases, the real demand for money also increases
| True |
| False |
Question 9
Commodity money is money that has value because
| of the intrinsic value of the commodity. |
| it is legal tender. |
| the government says so. |
| All of the above. |
Question 10
High-powered money is
| money held by business for investment. |
| total currency in circulation plus depository institution deposits at the Fed. |
| total currency in circulation. |
| government bonds held by the public and depository institutions. |
Question 11
U.S. M1 money includes
| currency held by the public. |
| checkable deposits. |
| travelerâs checks. |
| All of the above. |
Question 12
U.S. M2 money includes
| currency, time deposits, and government bonds. |
| savings deposits, small time deposits, and private bonds. |
| checkable deposits, savings deposits, and small time deposits. |
| retail money market mutual funds, small time deposits, and government bonds. |
Question
Money is different from other assets like capital and bonds in that
| money does not pay interest. |
| money has intrinsic value. |
| money is a better long term store of value. |
| All of the above. |
Question
If a personâs income doubles, we expect their cash holdings to
| double |
| more than double. |
| less than double. |
| decrease. |
Question 15
Real money demand does not change when
| nominal GDP changes. |
| the interest rate changes. |
| the price level changes. |
| All of the above. |
Question 16
All else constant, the price level rises when the supply of money increases.
| True |
| False |
Question 17
If the nominal interest rate were to increase, then
| money demand decreases and the price level increases. |
| money demand increases and the price level decreases. |
| the money supply and the price level would increase. |
| the money supply and the price level would decrease. |
Question 18
Real money demand is a function of real GDP and the nominal interest rate.
| True |
| False |
Question 19
The real return on money is zero.
| True |
| False |
Question 20
If the expected inflation rate is 5% and the unexpected inflation rate is 4%, the actual inflation is
| 1% |
| 9% |
| -1% |
| 1.25% |
Question 21
When the rate of growth of money is constant
| the inflation rate equals the growth rate of money. |
| the nominal interest rate rises. |
| real money balances are declining. |
| All of the above. |
Question 22
A decrease in the money growth rate in the market clearing model causes
| a decrease in the nominal interest rate. |
| an increase in money demand. |
| a decrease in the price level. |
| All of the above. |
Question 23
A decrease in the money growth rate in the market clearing model causes
| an increase in the nominal interest rate. |
| an increase in money demand. |
| an increase in the price level. |
| All of the above. |
Question 24
Under price level targeting the money supply becomes
| neutral |
| endogenous |
| exogenous |
| predetermined |
Q 25 During a recession, the interest rate falls tending to cause money demand to rise, but is at least partly offset by real GDP falling tending to cause money demand to fall.
| True |
| False |