PS102 Chapter Notes - Chapter 4: The Big Questions, Prenatal Development, Wireless

PS102B – Winter 2018
CHAPTER 4: HUMAN DEVELOPMENT
Developmental Stages
• Newborn: 1st month of life
Human Development
• The study of changes in behaviour and mental processes
o over time
o the factors that influence the course of those constancies and changes
The Big Questions
• Critical & sensitive periods
o Critical period = age where experiences must occur
▪ Ex. If do not learn a language by age 5, will not be able to learn the
language well
o Sensitive periods = optimal age range
▪ flexible
▪ Ex. Language best learned at age 4
• Nature & Nurture
o Is it the environment or heredity? … usually both!
▪ Lung and skin cancer (lifestyle/environment) VS brain and bone
cancer (genetics)
• Continuity VS Discontinuity
o Gradual or stages?
• Stability VS Change
o Do things remain constant
▪ Ex. Can a shy person become outgoing
▪ Personality traits = stable, however can change slightly
Mapping Change
1. Stages
• Discontinuous (qualitative) changes
• Ex. Crawling -> walking -> running
2. Continuous
• Gradual (quantitative) changes
• Keep getting better in same skill
• No distinctive changes
• Ex. Walking faster, more skill, more stability
3. No Change
• Remains constant
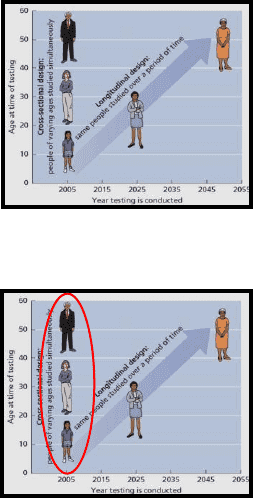
Research Designs
• Longitudinal
o Test same cohort over time
o PROS & CONS
▪ P: Same people (reduces variability
across samples)
▪ C: Time consuming
▪ C: People drop out
▪ C: Are changes generalizable to all people or just this group?
• Cross-Sectional
o Compare different ages at the same time
▪ Ie. Compare 60 yr olds VS 30 yr olds
memory capacity (to see how memory
changes as we age)
o PROS & CONS
▪ P: convenient (for researcher &
participant)
▪ P: Data from many age groups, but…
▪ C: Different cohorts grew up in different time periods
▪ C: Different experiences, cultural changes, environmental changes
• Ex. Wireless technology now prevalent
▪ C: assumes any changes found are a result of age
▪ C: cannot account for cohort differences (different life experiences)
• Sequential
o Test several cohorts as they age
o Blend btwn longitudinal and cross-sectional
o Cohort = group born at same time
o PROS & CONS
▪ of both the longitudinal & cross-sectional
▪ C: Very costly
Heredity & Prenatal Development
• Prenatal Period: the period of development from conception to birth
• Genes: basic building blocks of our biological inheritance
• Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): molecules in which genetic information is coded
• Chromosomes: strands of DNA; each human being has 46 chromosomes in 23
pairs
o In 1 pair: 1 from mother, 1 from father

• Allele: variation of a gene
o the two genes, one on each chromosome, that control the same trait
o Specifies traits (ie. Blue eyes VS brown eyes)
• Homozygous: two of the same alleles
o Ie. Freckles: both parents must have freckles for offspring to have freckles
• Heterozygous: two different alleles
• Discrete Trait: a trait involving a single gene pair
• Polygenic Trait: a trait involving multiple genes (ie. Height, weight, skin colour)
o Most human traits are polygenic
Genotype & Phenotype
• Genotype
o The sum total of all the genes that a person inherits
o Some genes are dominant, some are recessive
▪ Homozygous: 2 dominant (AA) or 2 recessive (aa)
▪ Heterozygous: 1 dominant, 1 recessive (Aa)
▪ Codominance: a person w/ heterozygous alleles may express both
their parents’ genes in their phenotype
• Ie. Type A mother + Type B father = Type AB child
• Phenotype
o The way in which the genes are actually expressed, or observed
characteristics of the genes
o Physical traits
• Ie. Ability to roll tongue – dominant trait…father can roll tongue & mother cannot roll
tongue = child can roll tongue
Document Summary
Developmental stages: newborn: 1st month of life. Human development: the study of changes in behaviour and mental processes, over time the factors that influence the course of those constancies and changes. The big questions: critical & sensitive periods, critical period = age where experiences must occur, ex. If do not learn a language by age 5, will not be able to learn the language well: sensitive periods = optimal age range flexible, ex. Language best learned at age 4: nature & nurture. Usually both: lung and skin cancer (lifestyle/environment) vs brain and bone cancer (genetics, continuity vs discontinuity, gradual or stages, stability vs change, do things remain constant, ex. Can a shy person become outgoing: personality traits = stable, however can change slightly. Mapping change: stages, discontinuous (qualitative) changes, ex. Crawling -> walking -> running: continuous, gradual (quantitative) changes, keep getting better in same skill, no distinctive changes, ex. Walking faster, more skill, more stability: no change, remains constant.

