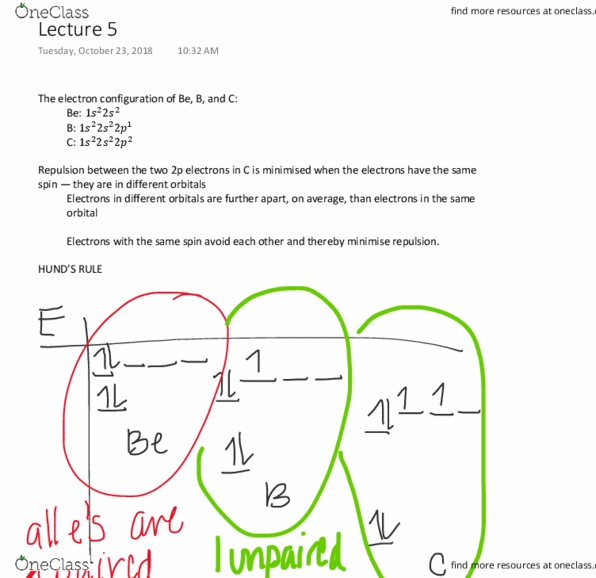
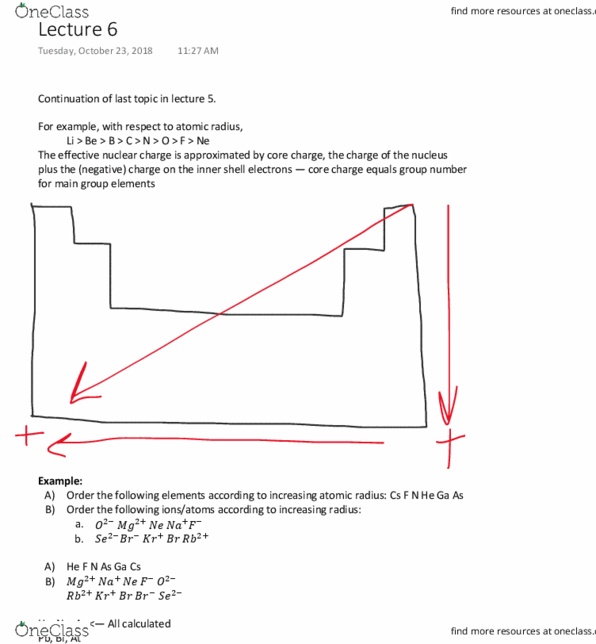
PLEASE READ THE WHOLE QUESTION
SIDE NOTE:
IN BIZARRO WORLD, the S subshell can only hold 2 electrons, the P subshell can only hold 4 electrons, the D subshellf can only hole 6 electrons and the F subshell can only hold 8 electrons.
We are trying to create a new periodic table based on these assumptions.
The modern periodic table is arranged the way it is because of quantum mechanics. That is, there are sections for each subshell, and the number of columns in each section are dictated by the number of electrons allowed in each subshell.
Imagine that you have entered an alternate dimension where the laws of quantum mechanics are different.The elements have the same symbols and even the same number of protons, neutrons, and electrons, but their arrangement on the Bizarro Periodic Table will differ greatly from our own. They use the same letters to designate the subshells (s, p, d, and f) even though their number of orbitals differ.
Consider these rules for the quantum numbers in Bizarro World:
n can be any whole number from 1 to infinity (this is the same as our world.)
l can be integer values from 0 to n.
ml can only go from 0 to l.
ms is the same as in our world (± ½)
Answer the following questions:
What subshells are allowed in the Bizzaro first shell? The second shell? The third shell? The fourth shell?
How many orbitals and electrons fit into the Bizarro s subshell? The p subshell? The d subshell? The fsubshell?
Based on this information, please draw what the Bizzaro Periodic Table might look like.
Draw the first 6 rows and include the s, p, d, and f subshell areas (include the f block between the s and dblocks, not separated).
Remember that the (n-1) rule for d subshells and (n-2) rule for f subshells still applies.
You donât have to list the atomic numbers or masses in each box, just the element symbols will be fine.
As a hint: the 6th row of your Bizarro Periodic Table should end with element 76, Osmium.
What elements would make up the Bizarro Noble gases?
What elements would make up the Bizarro Halogens?
How many total electrons would it take to fill the valence shell for any given atom?
Please give the Bizzaro electron configuration for the following elements. You may use Bizarro noble gas abbreviations for the core electrons if you like.
Fe
Ne
C
Se
W