MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 18: Minimax, Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research, Mean Value Theorem
MATH114 verified notes
18/28View all
17
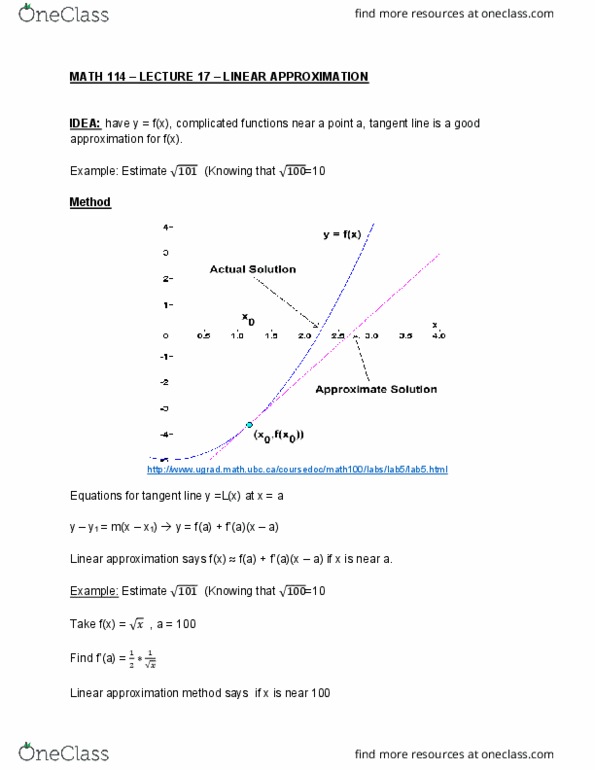
MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 17: Linear Approximation, Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research, Maxima And Minima
18

MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 18: Minimax, Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research, Mean Value Theorem
19
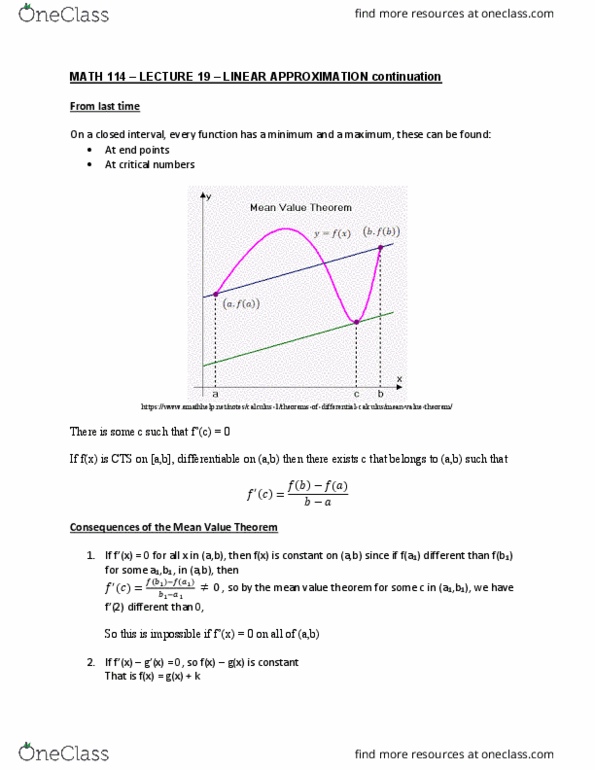
MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 19: Mean Value Theorem, Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research, Inflection
Document Summary
Math 114 lecture 18 linear approximation. Theorem if f(x) is cts function on a closed interval [a,b], then f(x) has a local max/min at x = c then f"(c) = 0 or f"(c) does not exist. Example: find critical numbers of f(x) = x1/3(x-1) with domain r. Solution: (cid:1858) (cid:4666)(cid:4667)=(cid:883)(cid:885) (cid:2870)(cid:2871)(cid:4666) (cid:883)(cid:4667)+(cid:2869)(cid:2871)=(cid:4666) (cid:883)(cid:4667) (cid:885)(cid:2870)(cid:2871) +(cid:2869)(cid:2871) (cid:885)(cid:2870)(cid:2871)(cid:885)(cid:2870)(cid:2871)=(cid:886) (cid:883) (cid:885)(cid:2870)(cid:2871) f"(cid:894)x(cid:895) dne (cid:894)does (cid:374)ot exist(cid:895) of x = 0 f"(cid:894)x(cid:895) = 0 if 4x -1 = 0 x = . Upshot if f(x) is cts on [a,b], then absolute maximum or minimum occurs at the critical points or endpoints. Method: f(x) cts on [a,b: find critical points of f + evaluate them compute f(c) with c critical, compute f(a) and f(b, compare: largest absolute maximum. Example: f(x) = x3 3x2 9x + 7 on [1,5] Absolute minimum at x = 3 (value is -20) Example: find the absolute maximum/absolute minimum of f(x) = (cid:4666)(cid:2870) (cid:2869)(cid:4667)




