MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 19: Mean Value Theorem, Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research, Inflection
MATH114 verified notes
19/28View all
Document Summary
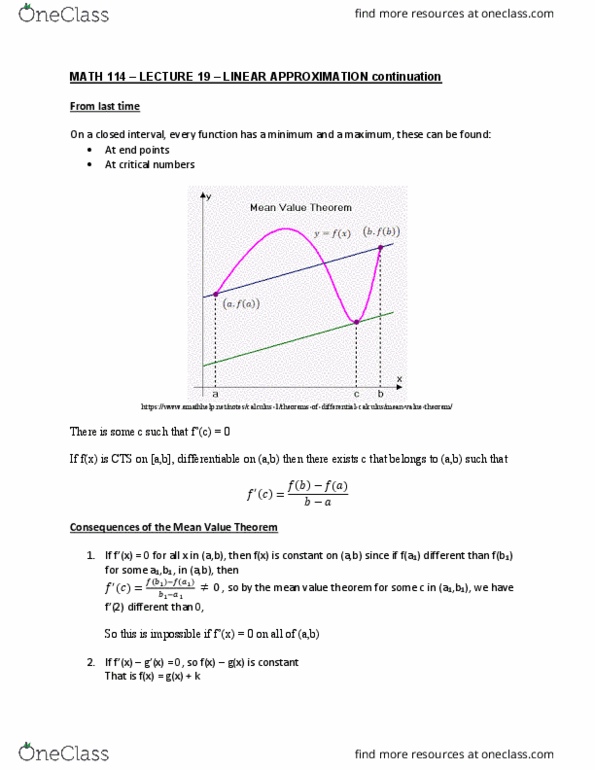
Math 114 lecture 19 linear approximation continuation. On a closed interval, every function has a minimum and a maximum, these can be found: at end points, at critical numbers https://www. emathhelp. net/notes/calculus-1/theorems-of-differential-calculus/mean-value-theorem/ There is some c such that f"(c) = 0. If f(x) is cts on [a,b], differentiable on (a,b) then there exists c that belongs to (a,b) such that (cid:1858) (cid:4666)(cid:1855)(cid:4667)=(cid:1858)(cid:4666)(cid:1854)(cid:4667) (cid:1858)(cid:4666)(cid:1853)(cid:4667) (cid:1854) (cid:1853) (cid:882) , so by the mean value theorem for some c in (a1,b1), we have. So this is impossible if f"(x) = 0 on all of (a,b: if f"(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) g"(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) = 0, so f(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) g(x) is constant. Idea: get i(cid:374)for(cid:373)atio(cid:374) fro(cid:373) f, f" a(cid:374) f"" to u(cid:374)dersta(cid:374)d ge(cid:374)eral (cid:271)eha(cid:448)iour of (cid:455) =f(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) Already know how to find: domain, asymptotes (horizontal and vertical, symmetry (even/odd) If f"(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) > 0 o(cid:374) a(cid:374) i(cid:374)ter(cid:448)al, the(cid:374) f(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) is i(cid:374)(cid:272)reasi(cid:374)g o(cid:374) the i(cid:374)ter(cid:448)al, a(cid:374)d if f"(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) < 0, the(cid:374) f(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) is decreasing http://www. analyzemath. com/calculus/problems/derivative_graph. html. This is be(cid:272)ause f"(cid:894)(cid:454)(cid:895) = slope of the ta(cid:374)ge(cid:374)t.