MAT 1300 Lecture Notes - Lecture 14: Antiderivative
MAT 1300 verified notes
14/14View all
Document Summary
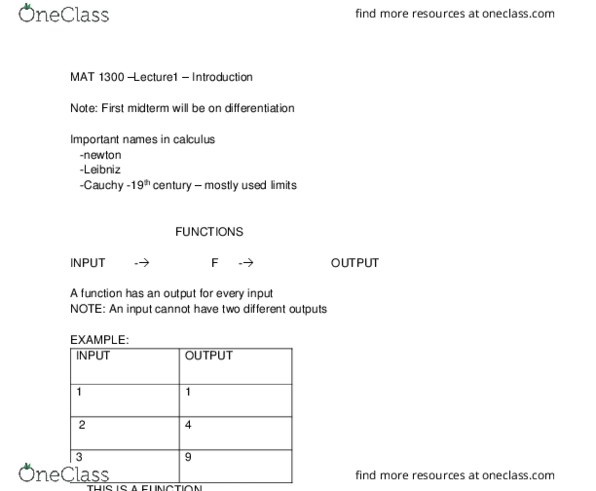
By the fundamental theorem of calculus to evaluate the definite integral b a f(x) dx. We can try to find an antiderivative f of f (meaning f"(x) =f(x) ) and compute f(b) -f (a) Notation : we write for f(b) - f(a) Basic rules for antiderivatives k f(x) dx =k f(x) dx (k real number ) [f(x)+- g(x)]dx = f(x)dx + g(x)dx x n dx = (1/n+1) (x n+1 +c) { n is not equal to -1} Special case : k dx = kx+c e x dx =e x + c. Example for each function find the antiderivative: 3x 4, 3x 2 +2x-7, 2 x (3x 4 ) dx = 3/5x 5 + 3 ln |x|+ c (3x 2 +2x-7 ) dx = x 3 +x 2 -7x+ c. X: 2/x 2, e x + 3/x (2/x 2 ) dx = -2/x+ c (e x + 3/x) dx = x 2 + 3 ln |x|+ c.